How Do EVs Work?
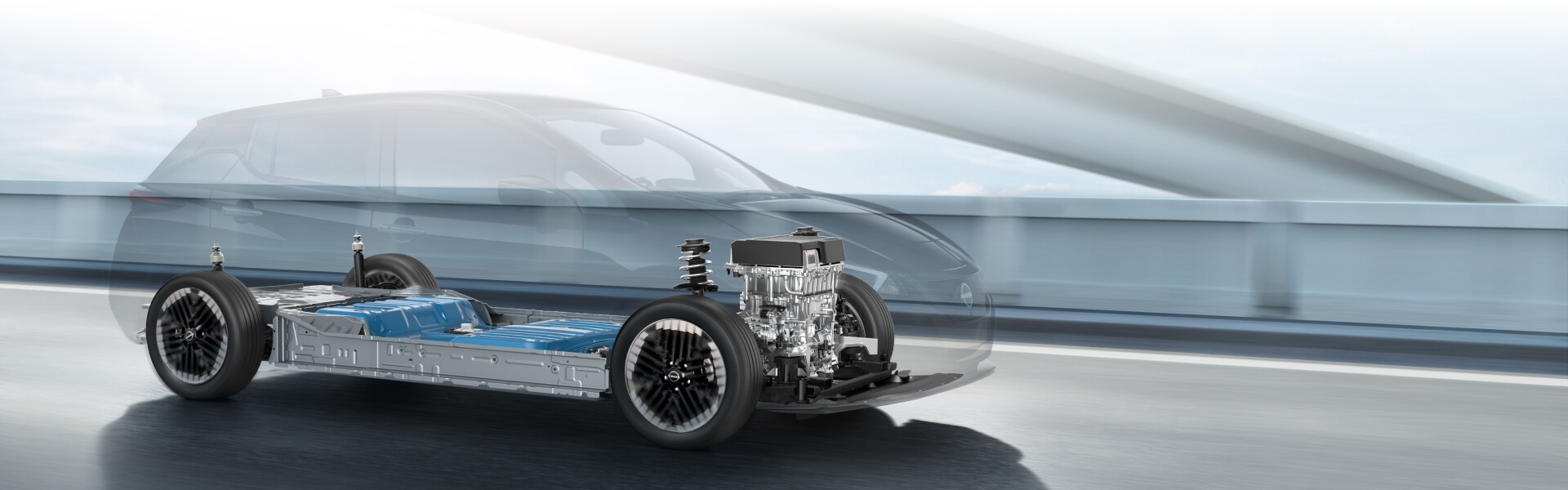
Unlike gas-powered vehicles, electric vehicles (EVs) do not require internal combustion engines to operate. Outfitted with an electric motor and rechargeable battery pack, EVs move along our roadways without burning up gasoline, without producing harmful exhaust emissions, and making less noise. If you’re thinking about making the switch to 100% electric driving, Fontana Nissan has detailed information on EVs and how going EV can work for you and your lifestyle.
The basics of electric vehicles
How do electric vehicles work? EVs receive energy from a charging station and store the energy in their batteries. These batteries give power to the motor which moves the wheels. Many electrical parts work together in the background to make this motion happen, but overall EVs have fewer moving parts than conventional gas-powered vehicles. Pretty simple.

From electricity to motion
Forget gas - Nissan EVs use electricity stored in rechargeable, high-voltage batteries to power an electric motor. The motor converts this electric energy into mechanical power that moves the wheels and allows the vehicle to operate.

Plug in, ride on
Electric vehicle batteries need to be charged with electricity. That electricity is supplied from a power outlet. All you need to do is plug in your EV at home or at a public charging station and let the grid do the rest.1 Soon you’ll be fully charged and ready for the road.2
Learn more about EV charging
Creating energy as you drive
Every time you step on the brakes, energy is lost in the form of heat. Regenerative brakes can capture that energy and store it in the battery so you can use it to let your EV take you even further.
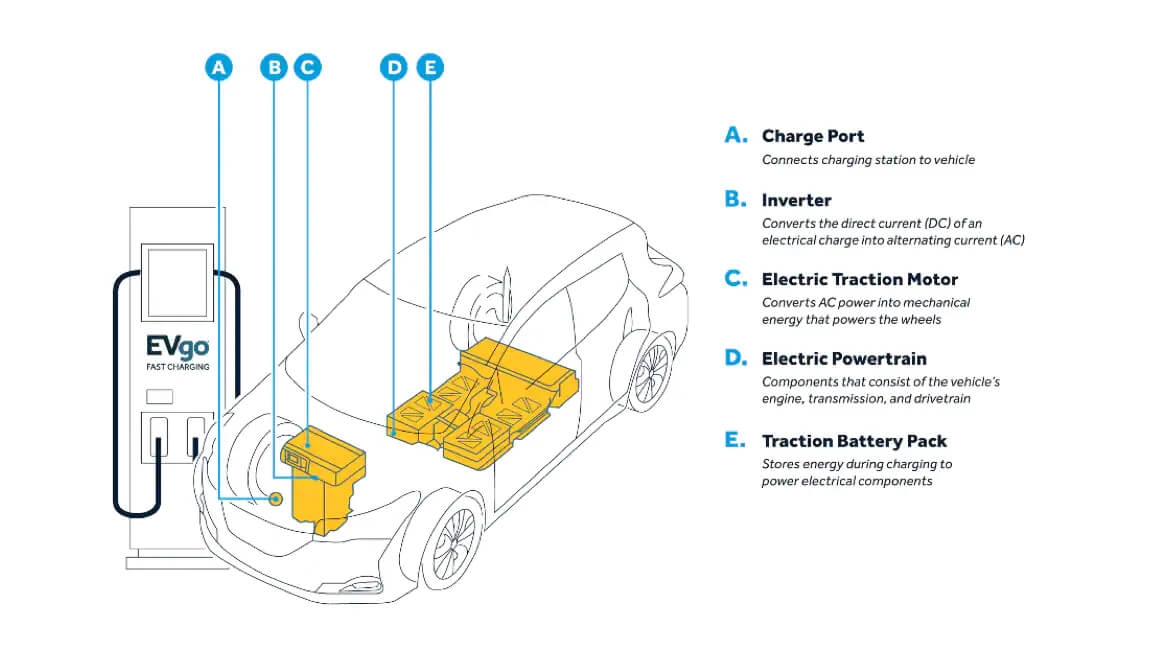
Learn more about EV BenefitsKey parts of an electric vehicle
Breaking down the key parts that make up an electric vehicle is essential to
understanding how they work. These key components include:
Types of Electric vehicles
Different types of electric vehicles provide drivers with a variety of features and varying benefits. The most common types of EVs include:
Battery electric vehicles (BEV)
A battery electric vehicle (BEV) is a zero-tailpipe emission electric vehicle that is powered solely from a battery pack. BEVs do not utilize internal combustion engines or gasoline to operate, so they do not produce harmful tailpipe emissions. These vehicles receive all their energy from Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) that draws electricity from the grid. Nissan ARIYA and Nissan LEAF are both Battery Electric Vehicles. For more information on ARIYA or LEAF, contact Fontana Nissan.
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEV)
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a low-emission vehicle that utilizes a small battery pack to assist an internal combustion engine. These vehicles receive most of their power from gas and cannot be plugged in to charge. Instead, their battery packs are charged through regenerative braking and using a generator connected to the gas engine. Although HEV’s can’t run solely on electric power, they maximize fuel economy by allowing the use of a high efficiency, lower power gasoline engine, running that engine in a more efficient way and only turning it on when necessary.
America's Best Commercial Van Warranty
A plug-in hybrid vehicle (PHEV) features both an electric traction motor and an internal combustion engine, which means they require EVSE charging and gasoline to operate. A PHEV runs on electricity until its battery pack runs out of power, in which case its internal combustion engine turns on and runs on gasoline.
NissanConnect EV Services
You’ll have everything you need to know about your EV’s range and charging available at your fingertips on your compatible phone with NissanConnect EV Services.3 Figure out estimated driving range, find charging stations, set charging reminders, start charging your vehicle, and more all through the NissanConnect app.4
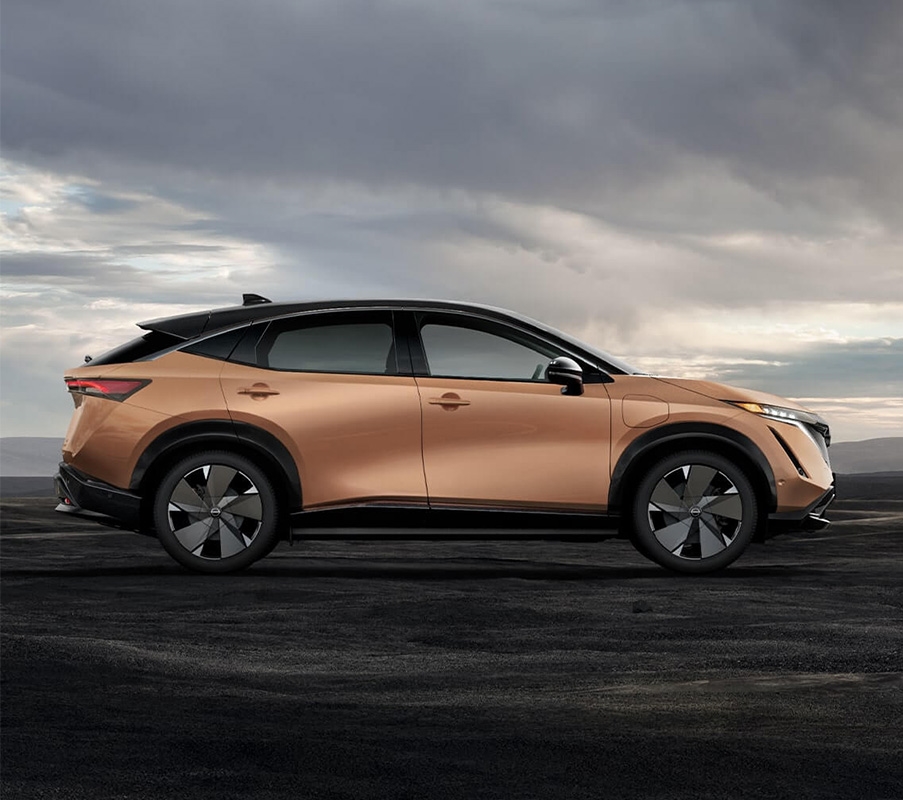

Nissan ARIYA
The All-New, All-Electric 2023 Nissan ARIYA is our newest EV. Depending on the trim you choose, the ARIYA offers up to 304 miles EPA estimated range.5 Battery size and two-wheel drive or e-4ORCE All-Wheel Drive provide different range options.
Range
304 miles
EPA estimated range for ARIYA VENTURE+
Battery Size
66 kWH
and available 91 kWh options
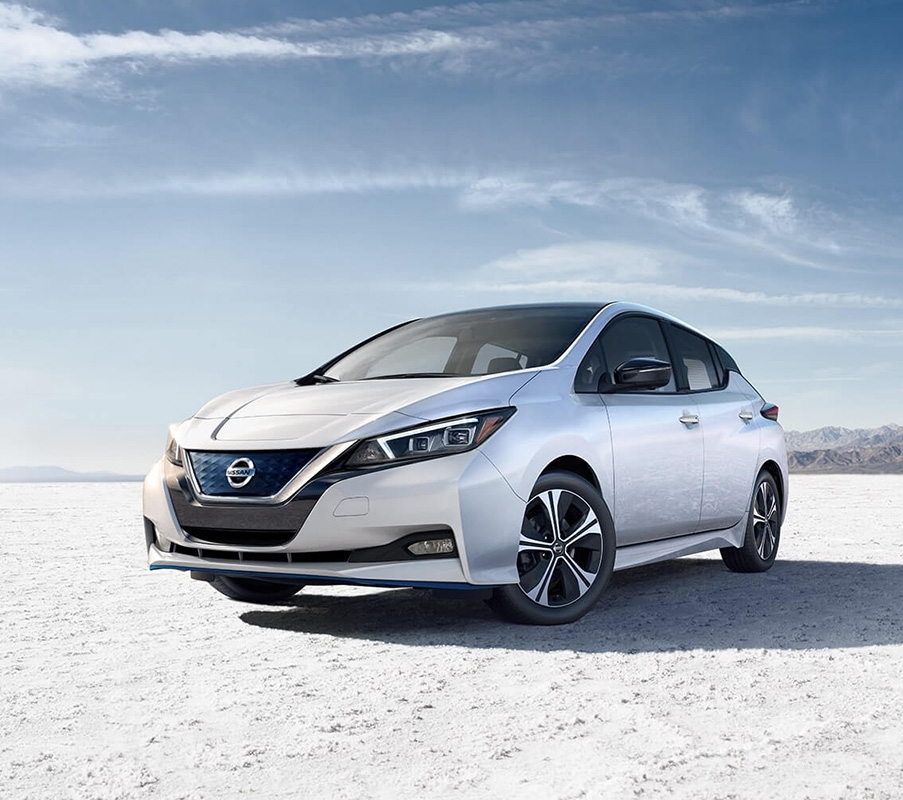

Nissan LEAF
TheThe LEAF is Nissan’s first-ever mass-produced 100% electric vehicle. The standard 40 kWh battery delivers 100% torque every time you step on the accelerator.
Nissan LEAF SV Plus model uses a 60 kWh battery that takes EV power to the next level.
Range
226 miles
EPA estimated range for LEAF S PLUS
Battery Size
and available 62 kWh options
and available 91 kWh options

